The medical statistics are relentless: this disease already affects the majority of the world's population! Therefore, almost 90% of women and more than 65% of men have varying degrees of clinical manifestations of varicose veins. Unfortunately, this disease is affecting younger people more and more - today there are reports that it has been found even in school-age children!
- innate tendencies;
- female pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalance;
- excess weight;
- Passive lifestyle.
Causes and signs of varicose veins
- increased venous pressure, determined primarily by venous hydrostatic pressure due to gravity, measured by the height of the fluid column, i. e. the distance from the heart to the measuring point on the leg. The pressure within the body cavity - the abdomen or pleura, which when increased (pregnancy, overweight, lifting and carrying heavy objects, etc. ), worsens the return of venous blood to the heart.
- Vein walls are relatively weak, which is genetically determined, but sometimes changes under the influence of venous inflammatory processes.
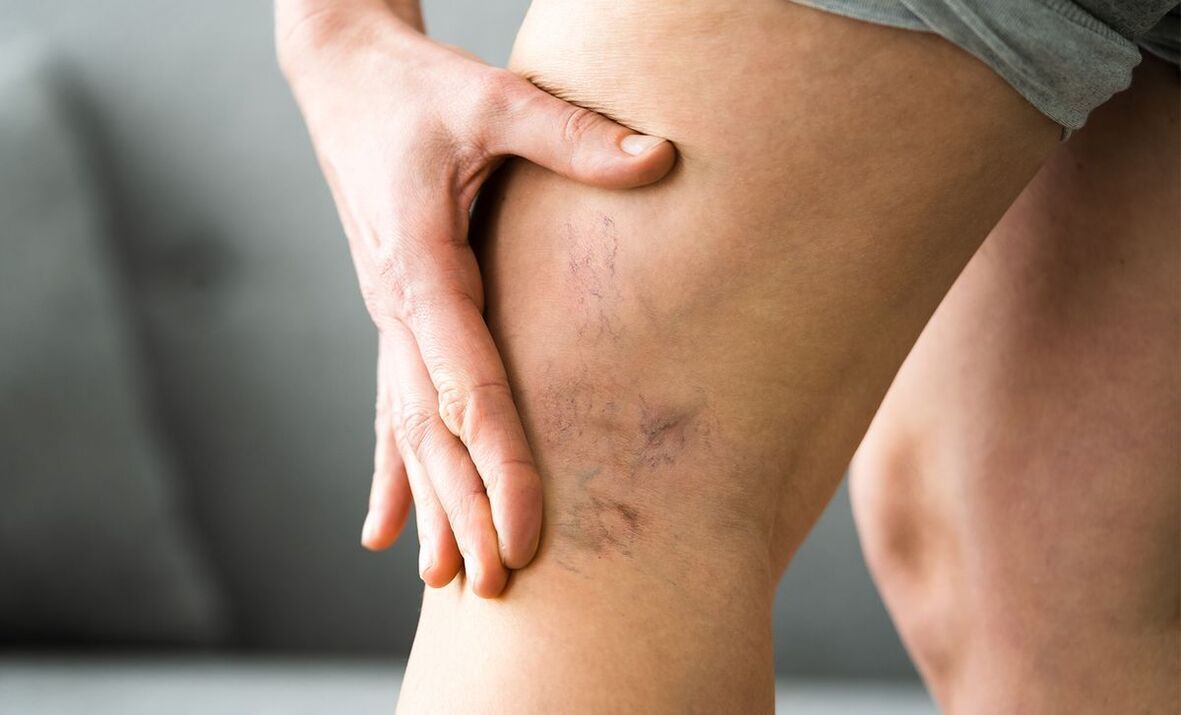
- In advanced cases, the saphenous vein becomes visually markedly dilated and tortuous - the formation of venous knots;
- There is a feeling of heaviness, fatigue, and fullness in the lower limbs and calves;
- The formation of telangiectasia (vascular "stars", "webs");
- Calf muscle cramps at night;
- swelling of feet and legs;
- Itchy, dry, hyperpigmented and bluish skin
- Nutritional, exudative, poorly healing ulcers occur.
Risk of varicose veins
Classification of varicose veins
The development of varicose veins
Beginning of disease development
subcompensatory stage
decompensation stage
Diagnosis of varicose veins
- examine;
- Duplex/triple scan.
- Research on some coagulation indicators and thrombophilia markers
Treatment of varicose veins
Conservative treatment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
surgical technique |
|
|
|
|
|
Prevent varicose veins
- Wear compression stockings;
- Maintain weight within normal range;
- Maintain an active lifestyle;
- Avoid standing for long periods of time;
- If there is a family history or symptoms of the disease are present, see a phlebologist promptly.